Major Neuropathological Correlates Of Alzheimer's Disease Are
Major neuropathological correlates of alzheimer's disease are. Neuropathological correlates of psychotic phenomena in confirmed Alzheimers disease. Solved Alzheimers disease is one of the most well-known forms of dementia. Current neuropathological criteria specify different numbers of plaques necessary for the diagnosis based on whether a clinical history of dementia is available and on age 27.
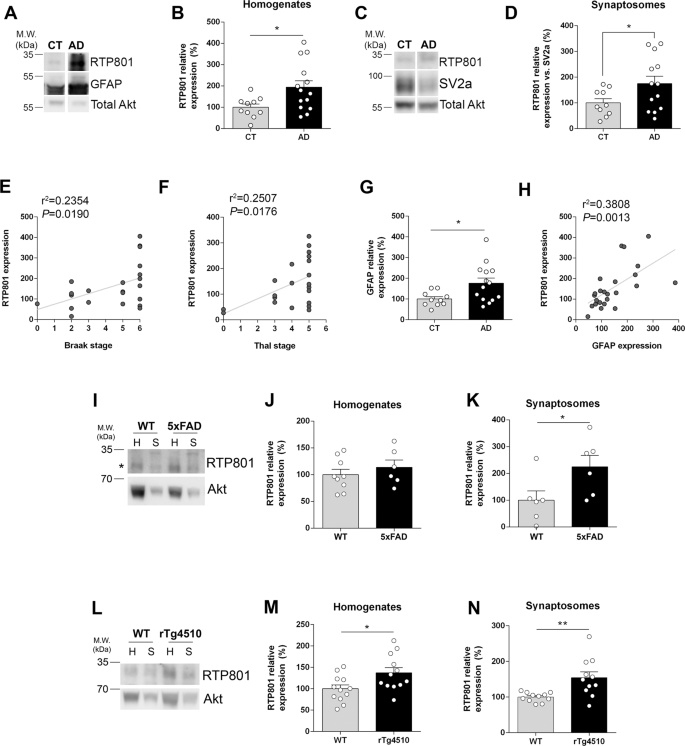
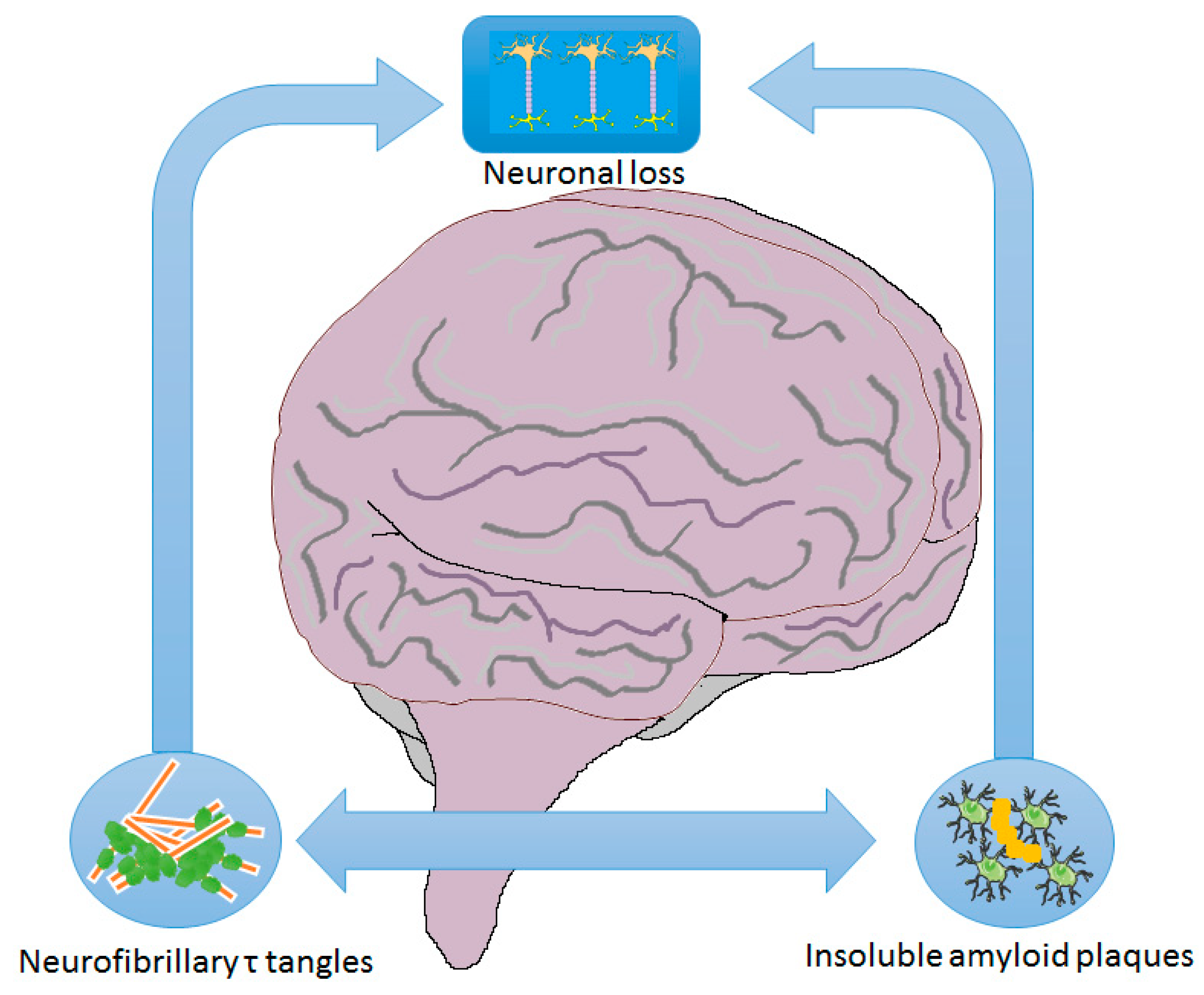
Solved Major neuropathological correlates of Alzheimers disease are. Förstl H1 Burns A Levy R Cairns N. The neuropathological hallmarks of Alzheimer disease AD include positive lesions such as amyloid plaques and cerebral amyloid angiopathy neurofibrillary tangles and glial responses and negative lesions such as neuronal and synaptic loss.
Thus the neuropathology of Alzheimers disease has been well described in terms of tangles plaques neuronal loss and disruption of specific sets of connections and these changes can correlate well with the clinical symptoms. Alzheimers disease AD features a long prodrome during which pathology accumulates without causing neurocognitive symptoms 1. We have studied the clinical and neuropathological correlates of apolipoprotein E genotype in a large group of Alzheimers patients.
Clinical and neuropathological correlates of depression in Alzheimers disease Depressive symptoms have been reported in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimers disease AD. Alzheimers Disease AD is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized clinically by progressive decline in memory cognition and function and pathologically by neuritic plaques NP neurofibrillary tangles NFT amyloid angiopathy CAA and neuronal and synapse loss. Lewy body diseases α- synuclein α-syn.
Depressive symptoms have been reported in patients with mild to moderate Alzheimers disease AD. Solved Neurofibrillary tangles found in the neurons of brains affected by Alzheimers disease contain. Alzheimers disease AD amyloid-β Aβ hyperphosphorylated tau tau.
Inheritance of the apolipoprotein E apo E epsilon 4 allele has recently been found to be associated with Alzheimers disease. 1Neurology Service Massachusetts General Hospital Boston 02114 USA. Pathological features of dementia reflecting Alzheimers disease diffuse and neuritic plaques and neurofibrillary tangles cerebrovascular disease Lewy bodies and neuronal loss having.
Recent evidence suggests that a noradrenergic deficit originating from neuronal degeneration in brainstem nuclei may represent an organic correlate of these disturbances. Alzheimers disease AD is a progressive neurodegenerative disease most often characterized by initial memory impairment and cognitive decline that can ultimately affect behavior speech visuospatial orientation and the motor system and it is the most common form of dementia 2.
Frontotemporal lobar degeneration tau TDP-43 ubiquitin.
Inheritance of the apolipoprotein E apo E epsilon 4 allele has recently been found to be associated with Alzheimers disease. Thus the neuropathology of Alzheimers disease has been well described in terms of tangles plaques neuronal loss and disruption of specific sets of connections and these changes can correlate well with the clinical symptoms. Inheritance of the apolipoprotein E apo E epsilon 4 allele has recently been found to be associated with Alzheimers disease. Recent evidence suggests that a noradrenergic deficit originating from neuronal degeneration in brainstem nuclei may represent an organic correlate of these disturbances. Lewy body diseases α- synuclein α-syn. Prospective longitudinal atrophy in Alzheimers disease correlates with the intensity and topography of baseline tau-PET β-Amyloid plaques and tau-containing neurofibrillary tangles are the two neuropathological hallmarks of Alzheimers disease AD and are thought to play crucial roles in a neurodegenerative cascade leading to dementia. Alzheimers Disease AD is a neurodegenerative disorder characterized clinically by progressive decline in memory cognition and function and pathologically by neuritic plaques NP neurofibrillary tangles NFT amyloid angiopathy CAA and neuronal and synapse loss. Memory and learning are fundamental components of cognition. We have studied the clinical and neuropathological correlates of apolipoprotein E genotype in a large group of Alzheimers patients.
1Neurology Service Massachusetts General Hospital Boston 02114 USA. These include cerebrovascular disease Lewy body disease TDP-43 proteinopathies and argyrophilic grain disease. Alzheimers disease is a clinical-pathological syndrome in which clinical dementia is due to Alzheimers disease-type neuropathological lesions. Förstl H1 Burns A Levy R Cairns N. Frontotemporal lobar degeneration tau TDP-43 ubiquitin. Solved Alzheimers disease is one of the most well-known forms of dementia. Solved Major neuropathological correlates of Alzheimers disease are.
















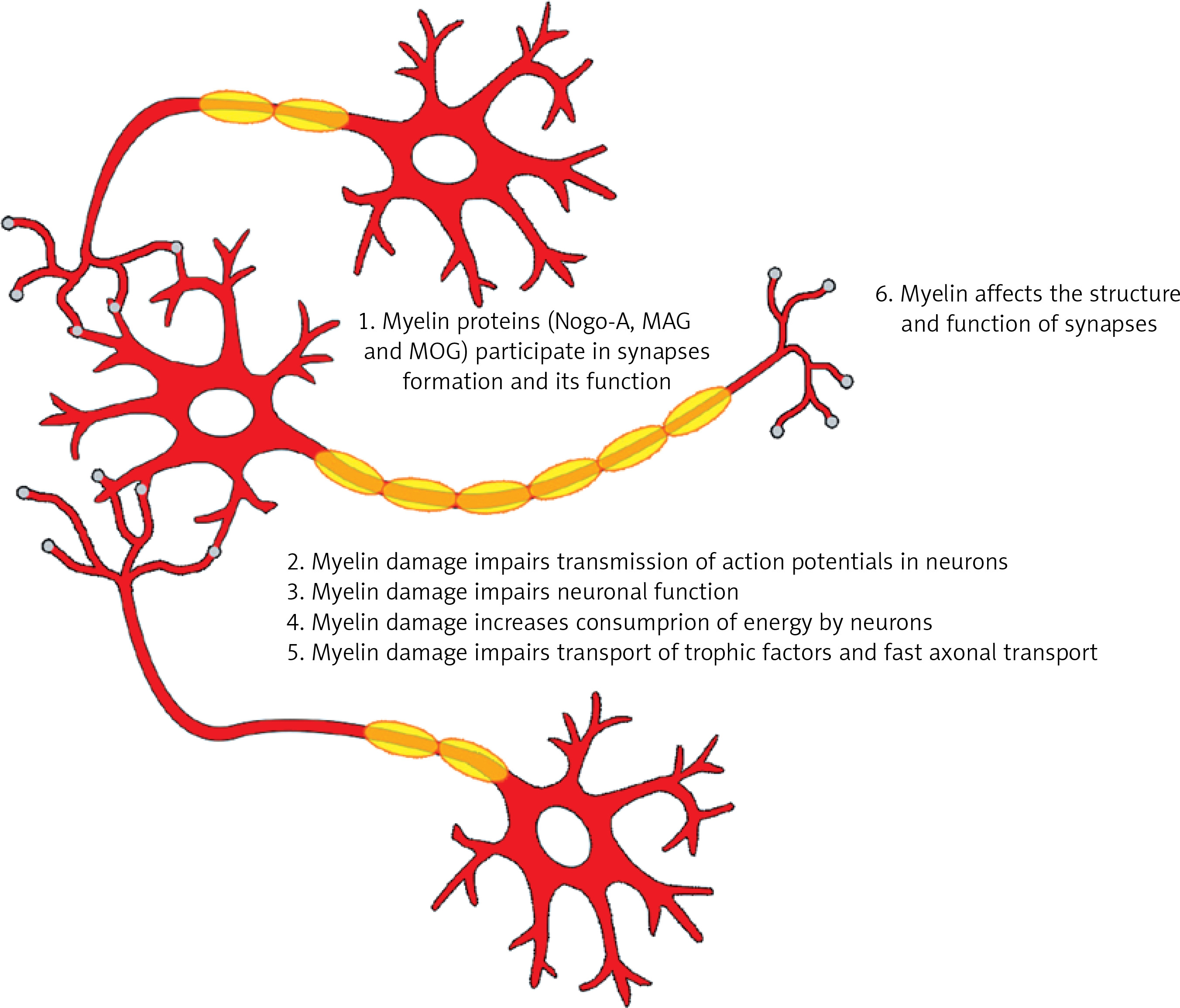
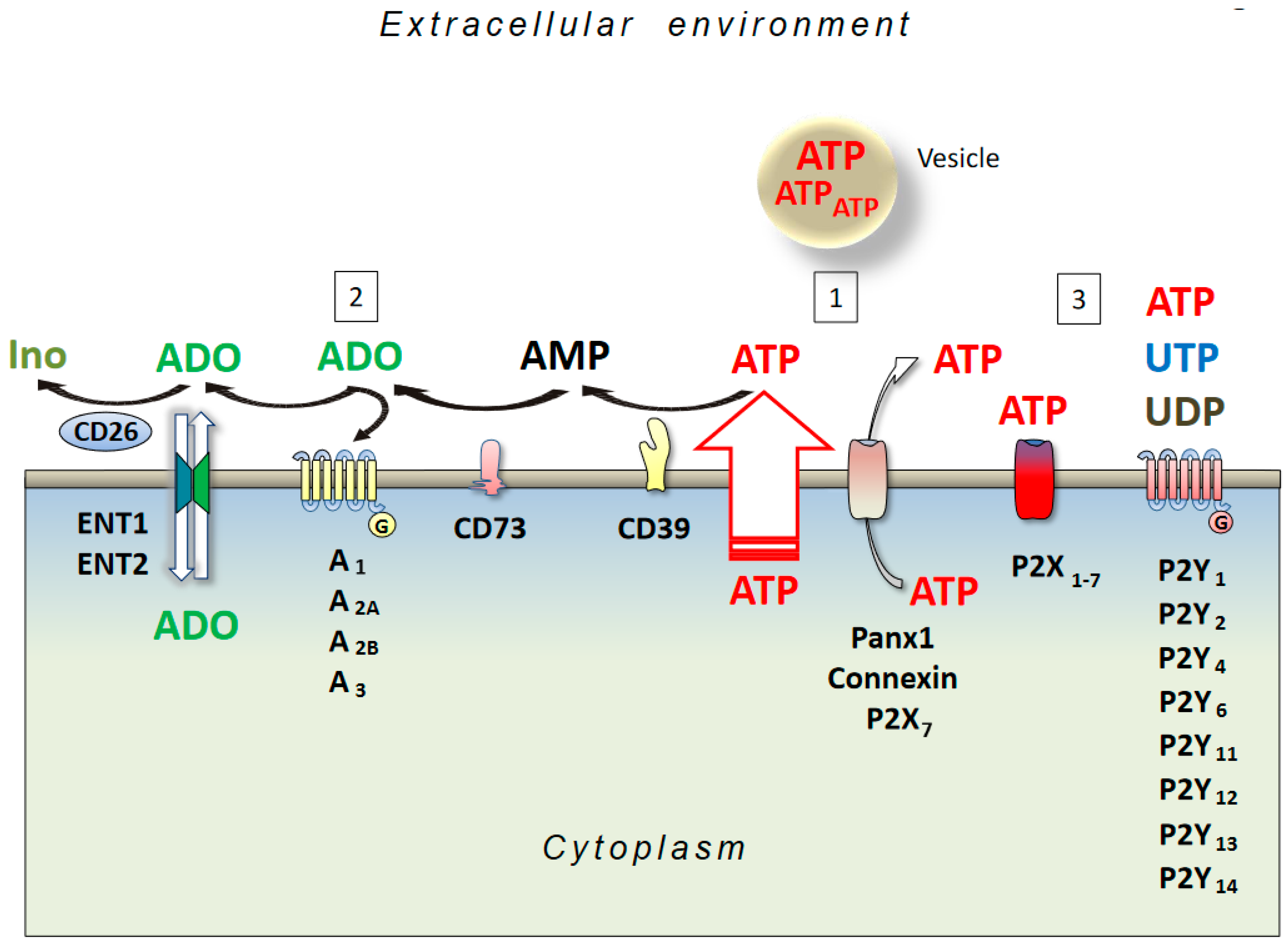



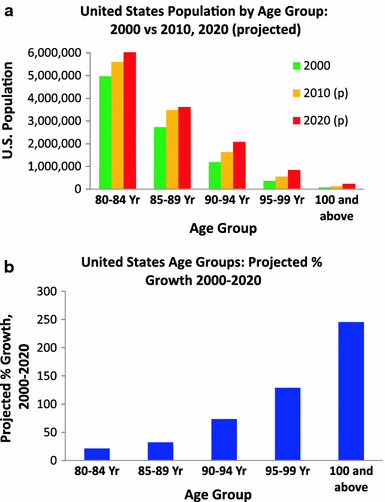
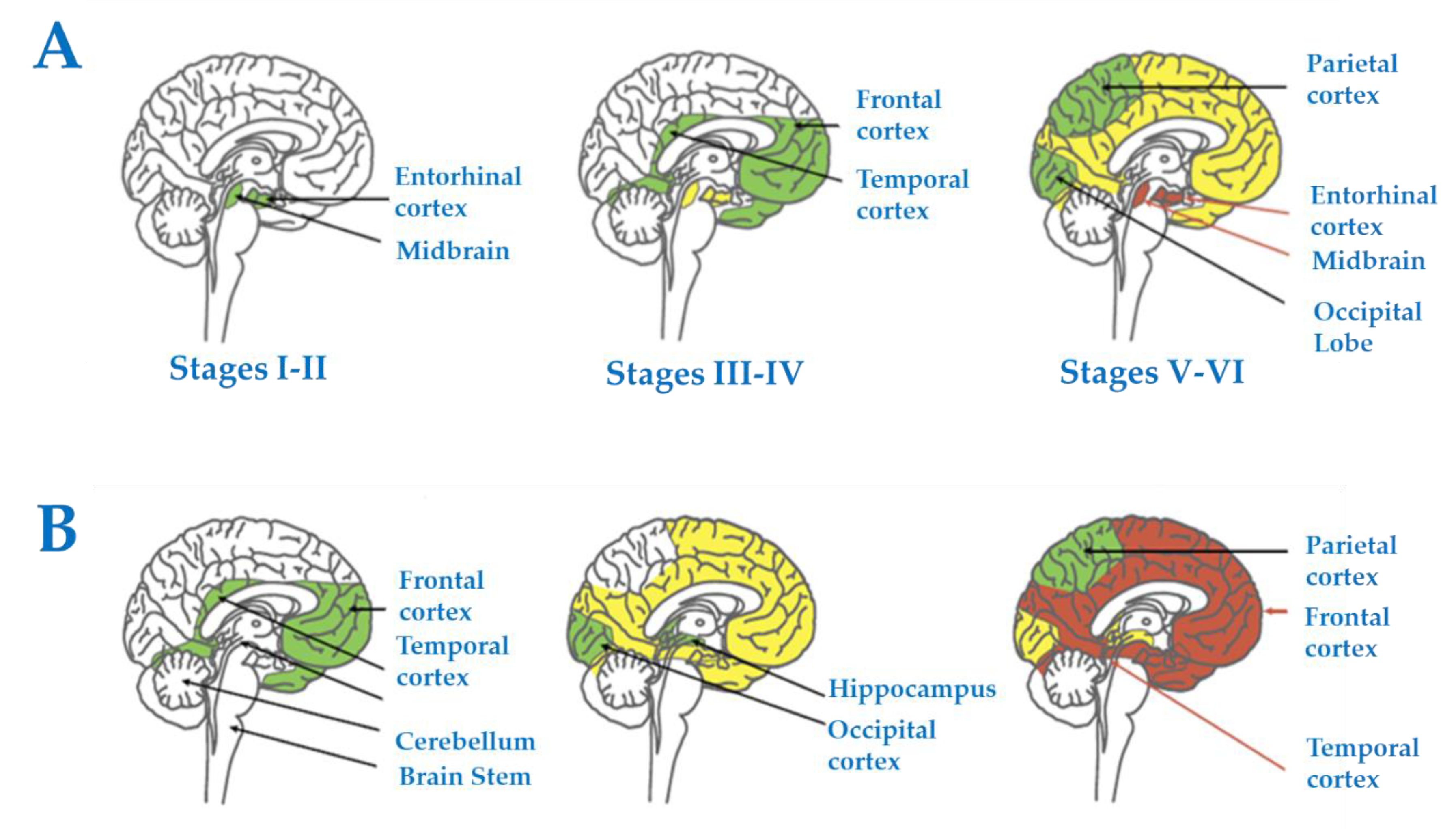





Post a Comment for "Major Neuropathological Correlates Of Alzheimer's Disease Are"